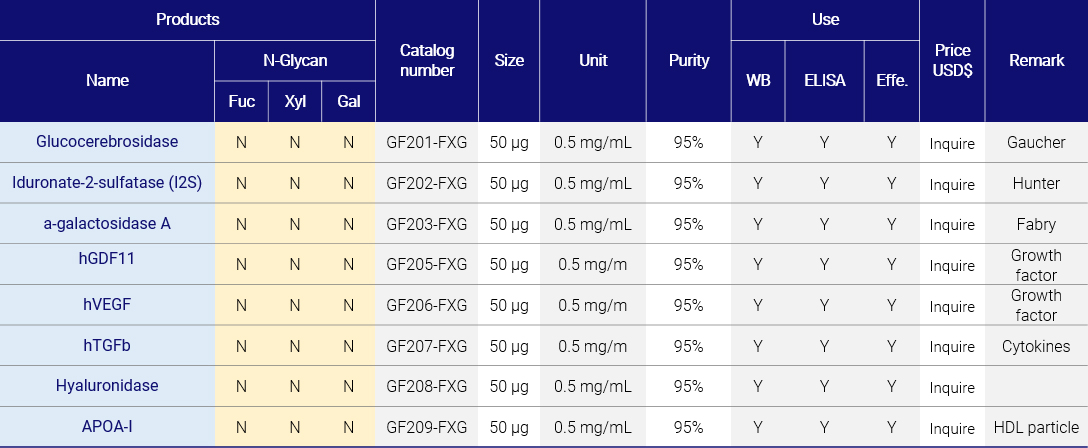
Protein Synthesis
-
Enhanced Safety and Reduced Contamination Risks:
- Plant-derived biopharmaceuticals offer a reduced risk of contamination with animal pathogens, addressing concerns related to zoonotic diseases.
- Plant-based expression systems provide a safer platform for producing biopharmaceuticals without the risk of animal-associated impurities.
- Plant cells are less susceptible to viral contamination, ensuring a higher level of product safety.
-
Cost-Effectiveness and Scalability:
- Plant-based production systems generally have lower production costs compared to animal cell cultures, leading to more affordable biopharmaceuticals.
- Plants offer scalability and higher production yields, allowing for larger-scale production of biopharmaceuticals to meet growing demands.
- Plants can be easily grown and cultivated in large quantities, reducing manufacturing costs and increasing cost-effectiveness.
-
Flexibility and Versatility:
- Plant-derived systems offer a wide range of expression options for producing complex proteins, including glycosylation patterns closer to human cells.
- The use of plants as bioreactors allows for easier genetic manipulation, enabling the production of a diverse array of biopharmaceuticals.
- Plants provide a flexible platform that can be tailored to express a variety of therapeutic proteins, including vaccines, antibodies, and enzymes.
These points highlight the benefits of utilizing plant-derived biopharmaceuticals, emphasizing safety, cost-effectiveness, scalability, and versatility over animal cell-based production methods like CHO cells.
Enhanced efficiency of Glyco-engineered mAb
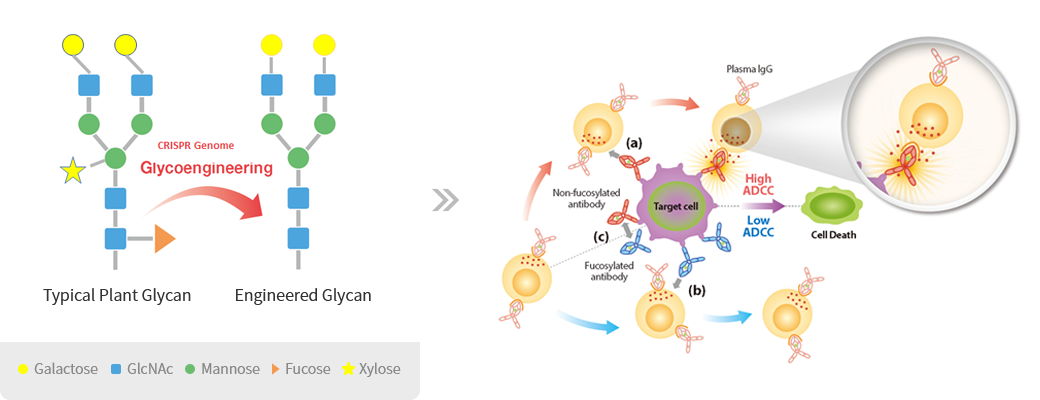
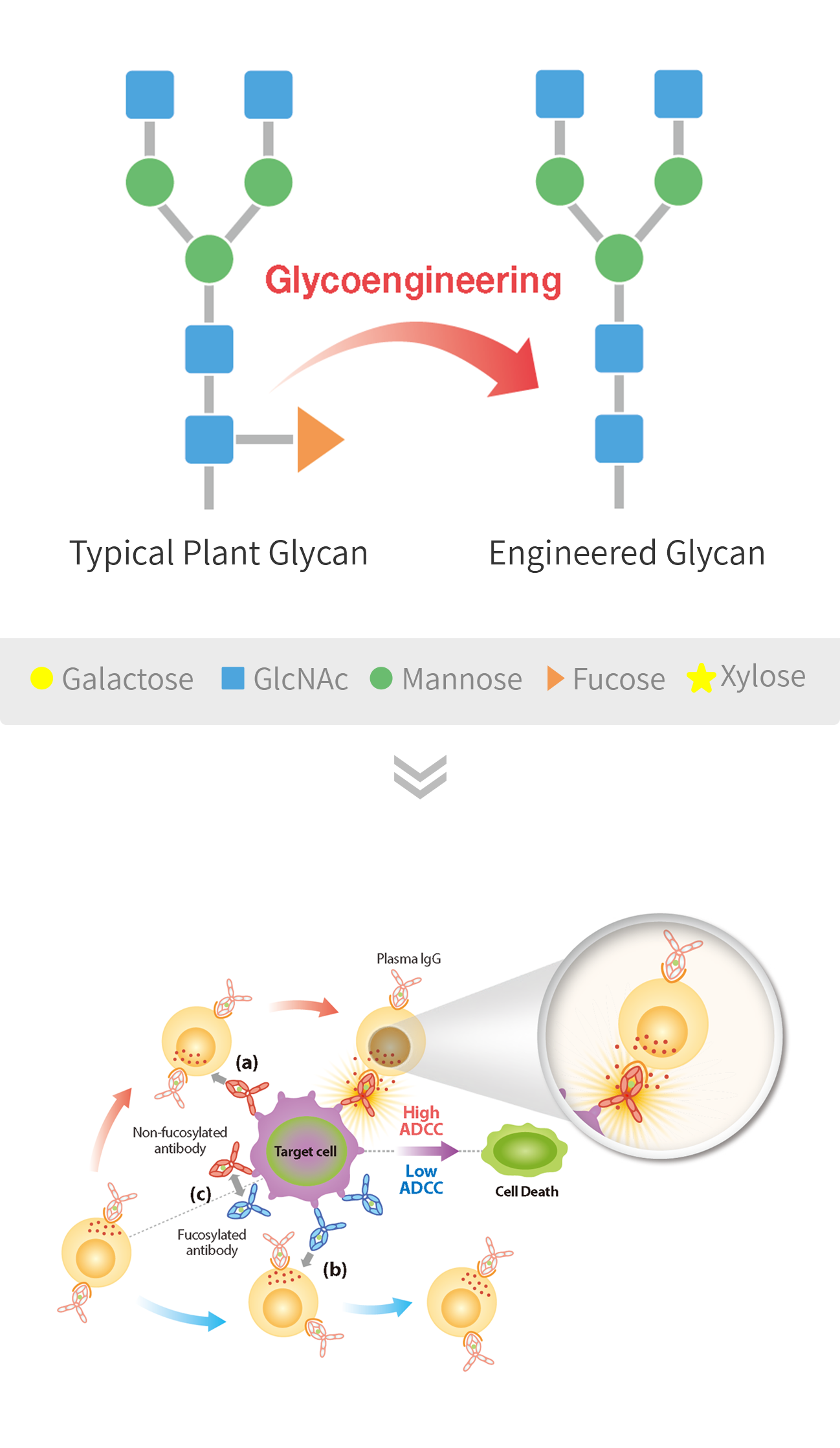
-
Enhanced Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity (ADCC):
- Afucosylated monoclonal antibody drugs exhibit enhanced ADCC, which is a crucial mechanism for the destruction of target cells by the immune system.
- The absence of fucose in the glycan structure increases the affinity of the antibody to Fcγ receptors on immune effector cells, leading to improved cell-killing activity.
- This enhanced ADCC capability results in more potent and effective elimination of target cells, potentially improving treatment outcomes.
-
Increased Therapeutic Efficacy
- Afucosylated monoclonal antibody drugs have demonstrated higher potency and efficacy in preclinical and clinical studies compared to antibodies with conventional glycan structure.
- The improved ADCC activity leads to enhanced target cell killing, allowing for better control of diseases such as cancer and autoimmune disorders.
- This increased therapeutic efficacy can translate into improved patient response rates and better overall treatment outcomes.
-
Flexibility and Versatility:
- Afucosylated monoclonal antibody drugs have shown promising results in a variety of therapeutic areas, including oncology, immunology, and infectious diseases.
- The enhanced ADCC activity opens up opportunities for targeting a broader range of diseases and expanding the applications of antibody-based therapies.
- By harnessing the potential of afucosylation, researchers can explore novel treatment strategies and address unmet medical needs across various disease indications.
These points highlight the advantages of afucosylated monoclonal antibody drugs over antibodies with conventional glycan structures, emphasizing the improved ADCC activity, increased therapeutic efficacy, and expanded therapeutic applications.
Nibentha Express™ platform
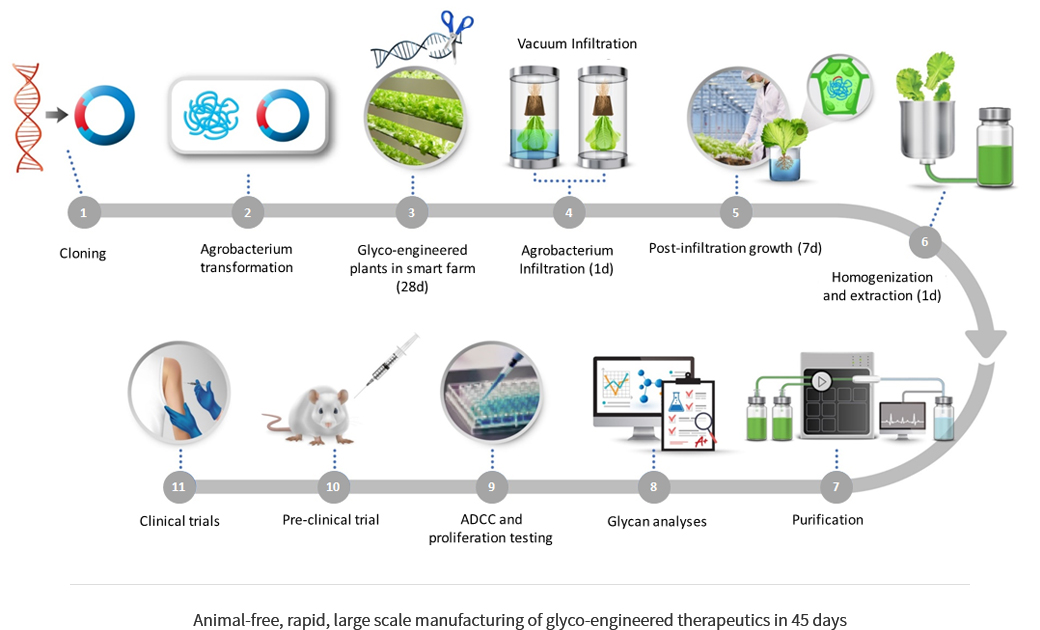
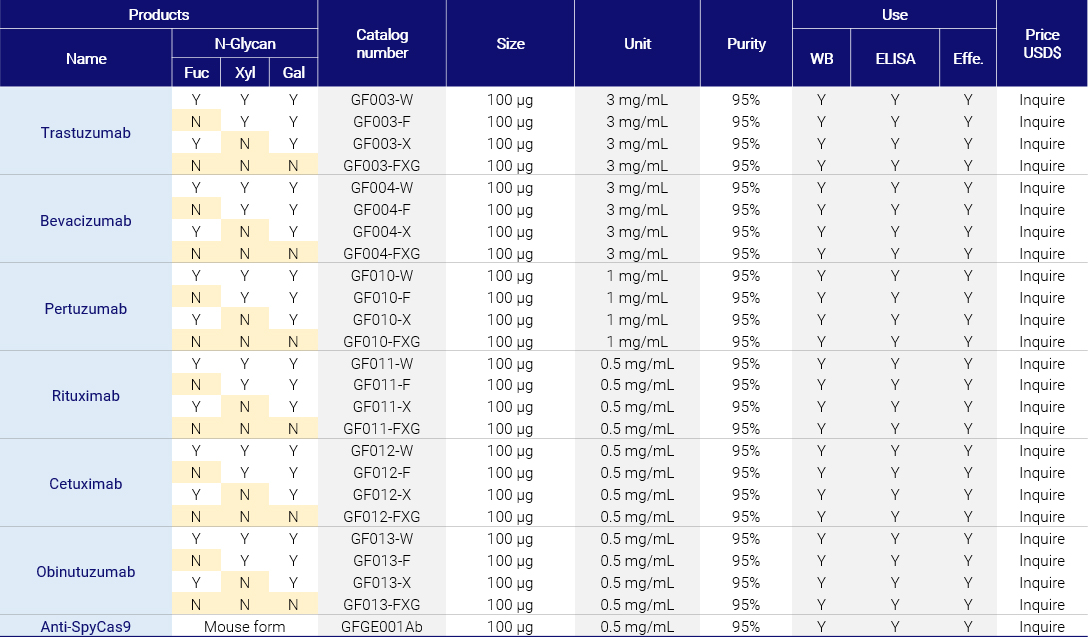
Plant-derived, glycoengineered monoclonal antibodies
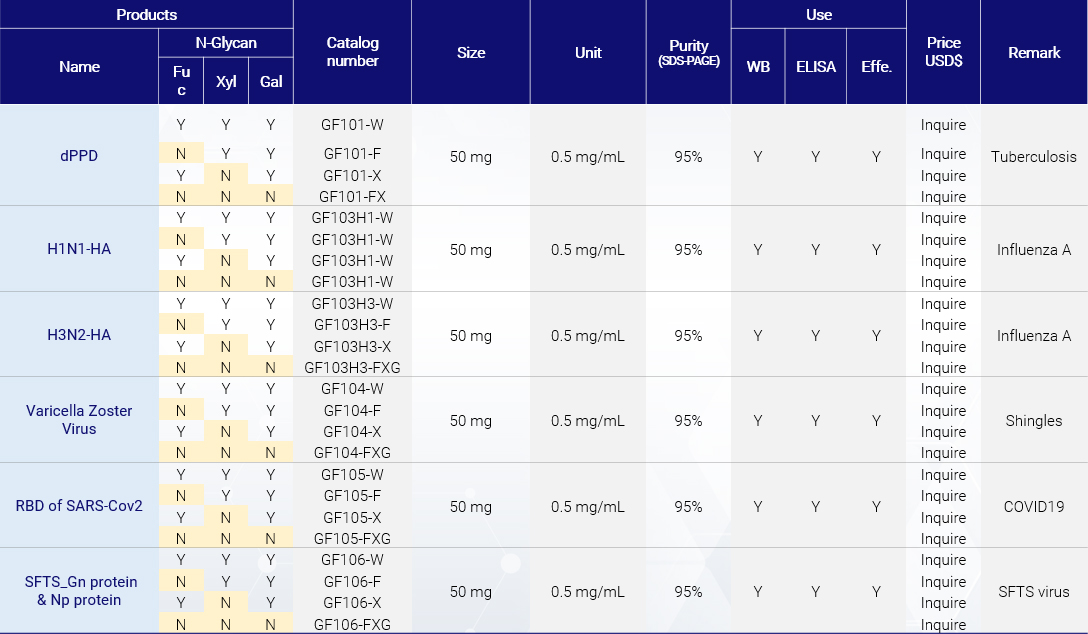
Plant-derived, glycoengineered antigens
Plant-derived, glycoengineered enzymes and other proteins